Bacillus Thuringiensis
Bacillus Thuringiensis is a type of spore-forming bacterium. The bacterium occurs naturally in all kinds of soils, coasts, mountains, deserts and meadows. There are thousands of different species of Bacillus Thuringiensis, which produce crystal proteins. These in turn are toxic to many pests, which is why the bacterium is often used in organic farming as a natural plant protection.
Bat Guano
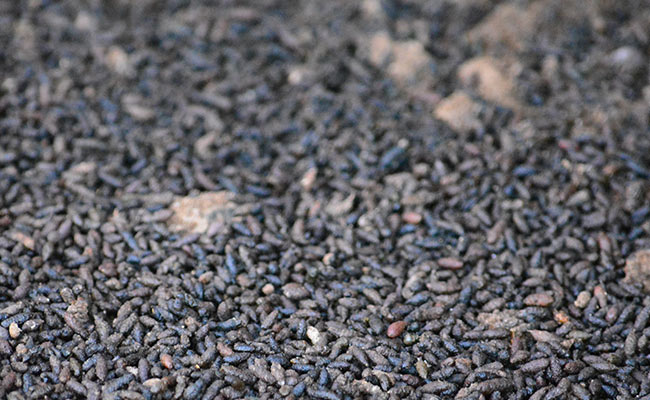

Bat guano (= bat guano) consists of the excrement of bats. It collects under their roosts and has long been used as a plant fertiliser. Bat guano provides important nutrients (phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium) and minerals for plants. Before it can be used, it must first be stored for a long time. The purely organic fertiliser is one of the strongest organic fertilisers in the world and is relatively expensive due to the difficult and lengthy extraction process. In addition to bat guano, there is also Seabird guano or seal guano, which have similar positive properties to bat guano.
Cottonseed meal
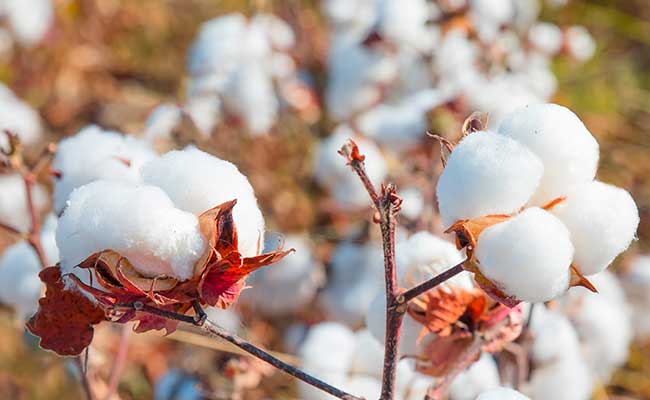

Cottonseed meal is an organic fertiliser made from hulled and de-oiled cottonseeds. It contains 7% nitrogen, 2.5% phosphorus and 1.5% potassium.
Bacteria
Bacteria are microscopically small, single-celled organisms. Some species are pathogens for dangerous infectious diseases in plants. Bacteria can exist as single cells, in chains or clusters, or as pairs. Bacteria are also very important in breaking down nutrients, with large parts of the nutrient cycle depending on these microscopic organisms. There are usually one million bacterial cells in a millilitre of freshwater and 40 million microorganisms in a gram of soil. Bacteria can be either helpful or harmful to plants, depending on their species and type.
Bactericidal
Bactericides are chemical components that kill or inhibit bacteria.
Pruning

Pruning is the process of trimming the branches and twigs of cannabis plants and thus influencing their growth behaviour. If pruning is done at the right time and with the appropriate technique, it can increase yields.
But pruning is also done to remove old or diseased leaves or to create more air in the growing space. In order for the upper flowers of the plant to grow as large as possible and retain all their vigour, some growers remove the lower branches with the small flowers. Pruning plants should always be done with disinfected scissors or a sterile knife. It is important not to remove too many leaves and branches at once.
You can read more about this topic here:
Irrigation system
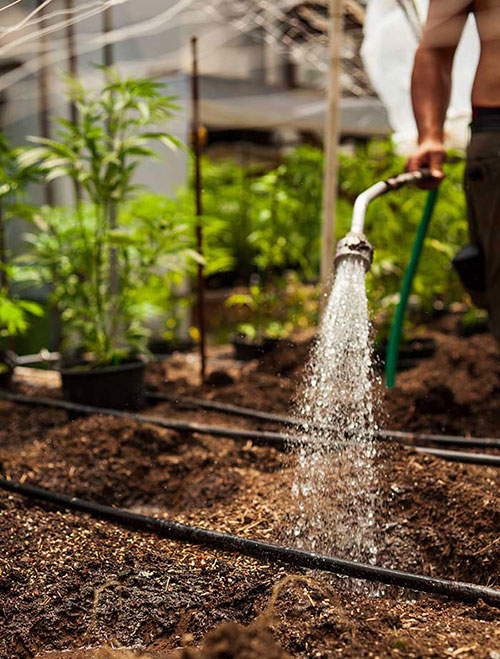

When growing cannabis, both indoor and outdoor irrigation systems can help save a lot of time and energy. For example, an indoor grow area of 1.5 m² with 16 vigorous plants in 11L pots needs between 35 and 95L of water per week. This can be lugged around. Large outdoor plants in large plant containers can even need an insane 10-35L of water per day. There may be several plant containers that need watering and so the whole thing becomes really exhausting and time consuming.
As long as the plants are still small, it doesn't matter much to carry the water from the bathroom to the grow room, as soon as the plants grow big it becomes a regular, exhausting job. Watering systems make life easier. There are different irrigation systems, each with advantages and disadvantages, but most of them are easy to implement: e.g. Drip irrigation systems, sprinkler irrigation, top-feed irrigation, Ebb and flow systems. Some irrigation systems are more suitable for outdoor growing than others. Some systems are mainly used for hydroponic cultivation, but can also be used on soil as long as a suitable setting is found with regard to the right amount of water and frequency.
Read more about irrigation systems, installation and important tips here:
Rooting hormones

Rooting hormones are special plant hormones that promote the formation of roots. These hormones are available either as powder, gel or liquid form and are used for the production of cuttings. Root hormones are also called auxin hormones. This type of hormone accelerates the growth of cuttings by helping to switch from the production of green stem cells to the production of root cells. Rooting hormones increase the chance of successful rooting of cuttings. They make propagation of unusual phenotypes easy and fast. You can find out how to make cuttings yourself and how to use rooting hormones properly here:
You can find out more about making cuttings here.
Bisabolol

Alpha-bisabolol is a cannabis terpene that is also produced by the chamomile flower. Bisabolol is known for its light, sweet and floral aroma and also has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anti-irritant and analgesic properties. This terpene, also called levomenol, has been used in cosmetics for centuries for its healing properties.
BHO
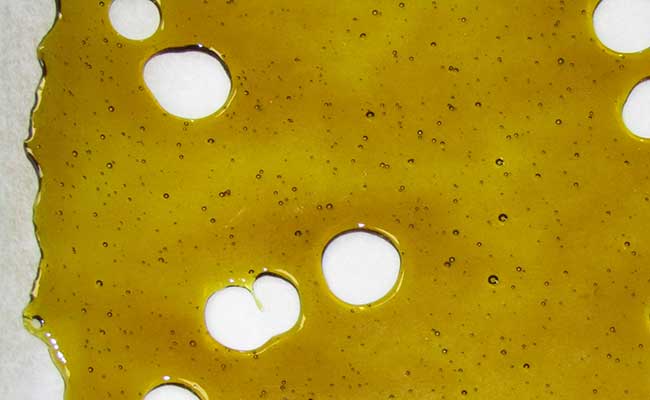

Butane hash oil (BHO) is a cannabis extract with a very high THC and cannabinoid content. BHO has an average THC content of 60-90%. With the help of purified Butane gas the resin is dissolved from the flowers. Mostly dried flowers are used for BHO. There are many names for different BHO products, for example: Honey, Wax, Shatter, Cannabis Oil. When used correctly, BHO is relatively pure. In the production of BHO, a Extraction tube preferably glass or stainless steel and purified butane gas.
All important information about the production of BHO can be found here:
Biodegradable
Products and fertilisers that are biodegradable can be decomposed naturally and with the help of bacteria.
Sheet

The leaves of cannabis plants fulfil three important tasks: Photosynthesis, gas exchange and transpiration. The leaves should always look juicy green and fresh. Changes in the leaves are in most cases an indication of a disease, poor growing conditions, a Deficiency symptoms or an overdose of one or more micro- or macronutrients.
All important vital functions of a plant are maintained by the leaves. The leaves convert (sun) light into energy and transpiration removes excess water from the plant. Through evaporation on the leaf surface, the moisture is released back into the environment.
Foliar fertilisation
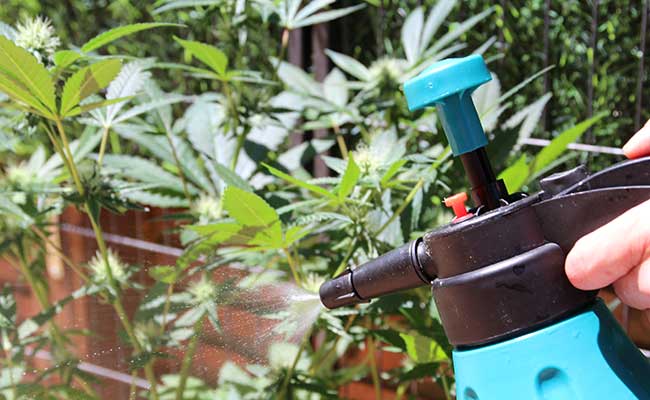

For foliar fertilisation, special liquid nutrient fertilisers diluted with water are sprayed onto the leaves. The dissolved nutrients are absorbed by the micropores on the top and bottom of the leaves.
Find out more about foliar fertilisation here:
Aphid

Aphids are pests that can also infest cannabis plants, especially outdoors. Aphids are up to 3 mm in size, have a soft-skinned body and are sucking pests.
Bleach
Household bleach can be mixed with water to disinfect equipment, surfaces and the growing space. Bleach can eliminate harmful fungi, bacteria and pests. It must not be used on the plants themselves because it can severely damage them.
Blunt
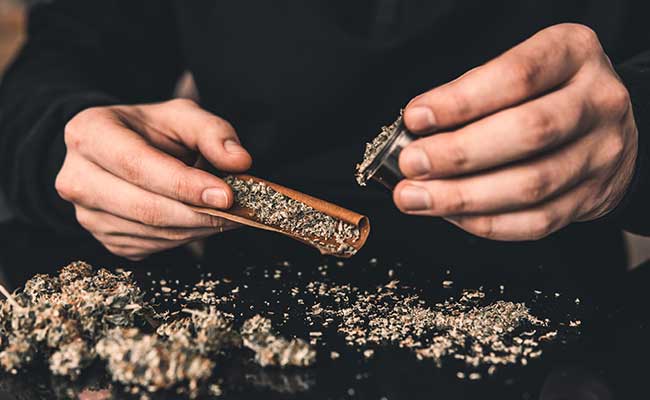

A blunt is a type of joint that is rolled with a usually pre-made tobacco or hemp leaf. Blunts are either naturally flavoured with tobacco or hemp or with different flavours. For example Juicy Jay`s and Kings Blunts offer pre-made blunts for rolling with many flavours.
Flower booster
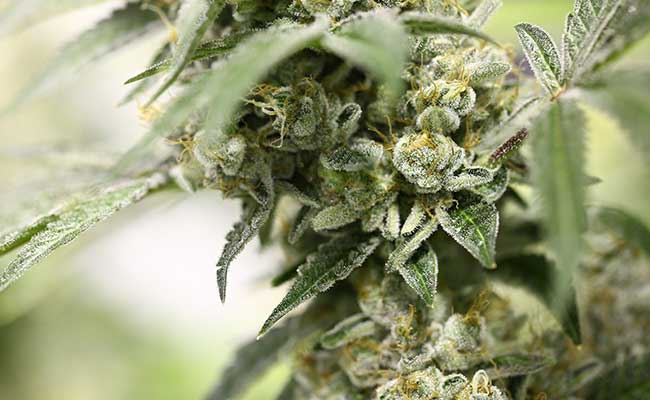

Flowering booster are special additives and fertilisers for cannabis plants that increase and promote flower formation and size.
Flowering fertiliser
Cannabis plants need a fertiliser with a different composition in the flowering phase than during the growing phase. In the flowering phase, the plants need a fertiliser with a high phosphorus content, which promotes flowering.
Flower
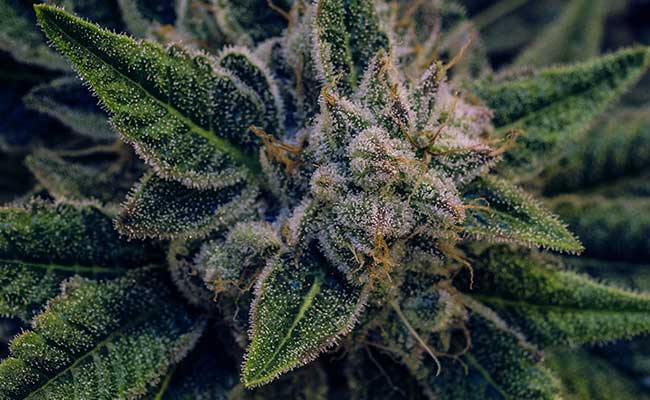

In the cannabis plant, the female flower consists of a mass of ovaries very close together.
Flowering
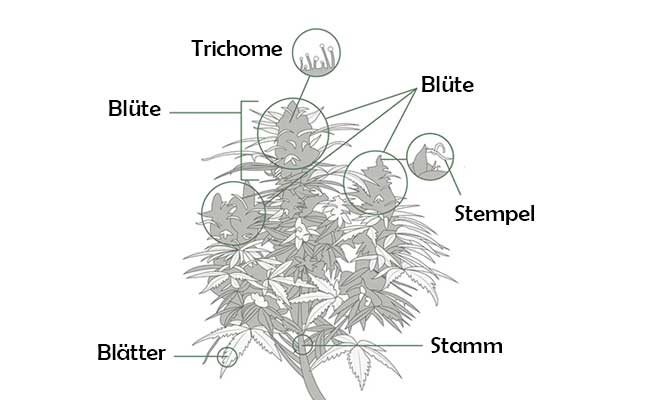
Depending on the cannabis variety and type, the flowering time takes between 7 and 13 weeks. While Indicas and Indica dominant strains mostly need a flowering time of 7-9 weeks, some Sativas need up to 13 weeks and more.
Autoflowering strains have a relatively long flowering time and are only in the vegetative stage for a short time. Generally, the photoperiod cannabis plant comes into flowering when it receives 12 hours or less of light per day.
The cannabis plant goes through four stages of flowering: The first stage of flowering is pre-flowering. The first signs of female flowers with only two white stem hairs appear. They emerge at the stem connections of the plant. This phase lasts about 2-3 weeks. As the flowering progresses, more flower spikes and small flowers form. Resin glands develop and the calyxes become larger and larger. At the beginning of the flowering phase, cannabinoid production is briefly reduced and then accelerates considerably. The flowers gain volume and become denser. At the end of the flowering period, THC production is at its highest and the flowers are ripe. The last ripening phase lasts about 14 days.
Flowering is the end of the cannabis plant's life cycle. In the wild, the flowering of cannabis plants starts in autumn, when the days become shorter.
There are both male flowers and female flowers on cannabis plants. Most growers are only interested in the female flowers, which can produce a psychoactive effect and have a variety of medicinal benefits. Feminised seeds only produce female plants.
Read more about flowering time and ripeness here:
- Light cycle in the flowering period and floral growth
- Pre-flowering, initiation of flowering and flowering phases
Ground temperature

The ideal soil temperature for cannabis plants is 18°-23° C. An increase in soil temperature (in the ideal range) leads to an acceleration of chemical processes and nutrient uptake. A soil temperature above 24° C leads to overheating of the roots and increased pressure within the roots. This in turn can cause damage to the root area. Already from a soil temperature of 24° C the roots dry out quickly and must be supplied with sufficient water to avoid damage. In summer, direct sunlight can cause the planters to overheat. Avoid this by using white pots, place plastic pots in a larger clay pot to protect the roots from direct sunlight and heat. In the growing room, the temperature should be kept around 24°C so that the pots do not heat up too much. An irrigation system can help to cool the soil.
A soil temperature below 10° C slows down the uptake of water and nutrients by the plants. This can easily lead to overwatering, which can also damage the roots. Increase a too cool soil temperature by not placing the plants directly on the soil but e.g. on Styrofoam, use a fan heater or another heating system for the growing room, use heating cables or heating mats to bring the root zone to the desired temperature. For example, with the Rapitest you can easily and quickly determine the soil temperature. If the temperature of the substrate is not high enough at germination, seeds will not germinate! Too high a temperature will cause the seeds to dry out before they can develop.
Bokashi
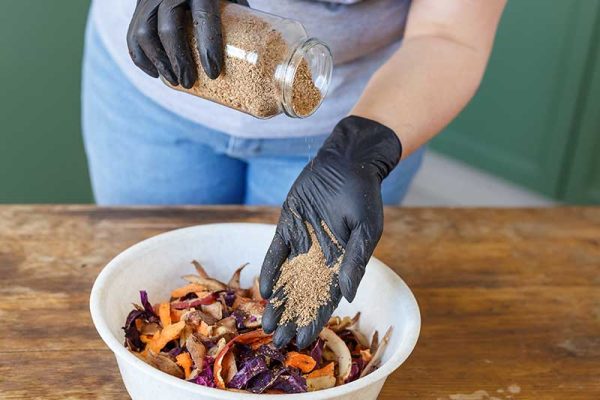

The Bokashi composting is a natural composting method that uses inoculated bran to naturally ferment and break down certain food scraps or plant parts. The composted product improves the soil and is fully loaded with important nutrients for the plants.
The Bokashi composting method is based on the isolation and cultivation of specific strains of bacteria. The unique bacterial process was developed in 1982 by Dr Teuro Higa, professor at the University of Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan. The entire process takes about 7 to 10 days, which is ten times faster than conventional composting methods. It also produces no harmful odours, heat or greenhouse gases.
You can learn more about Bokashi composting here:
Bong
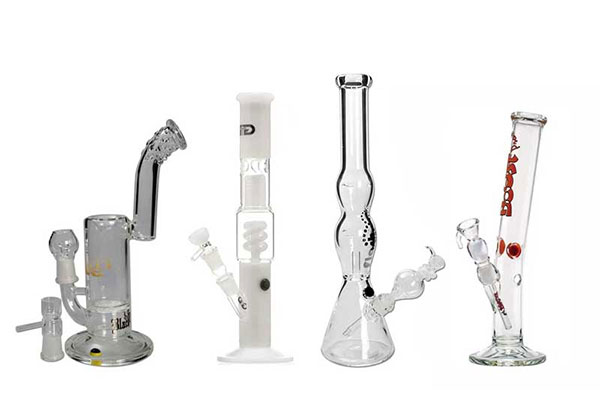

A Bong is a water pipe used for smoking cannabis. A bong consists of a bong head, a tube, a water chamber and a mouthpiece. Flowers or a mixture of flowers and tobacco are put in the bong head, which is then lit. The smoke is filtered through the water before it is inhaled.
Some bongs are also equipped with a perculator system or ice notches to further cool the smoke. Bongs are available in a variety of sizes, shapes and colours. They can be made from a variety of materials such as wood, bamboo or clay. However, most bongs are now made of glass. High-quality bongs are made of borosilicate glass, which is also used in laboratories and can be brought into contact with hot water without the glass cracking.
Bongs are easy to use and provide a strong and unmediated hit. Studies have shown that bongs can actually filter certain pollutants from the smoke, though certainly not all. They remain a matter of taste, some love them, others prefer joints.
You can find out more about bongs, the different types and how to use them here:
Borneol

Borneol is a terpene found in cannabis plants that makes a camphor-like and woody aroma. Borneol has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, especially when used topically. Borneol is found not only in cannabis but also in wormwood and the cinnamon tree. We find it especially in cannabis strains like K13 and in many Haze strains.
Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a versatile and flexible glass that is used for many industrial purposes due to its strength and properties. Like conventional window panes or drinking vessels, it is made with sand, sodium carbonate and limestone with the addition of boric oxide. It is characterised by its resistance to rapid temperature fluctuations and is therefore often used in laboratories or in the manufacture of bongs and smoking devices.
Botrytis (grey mould)
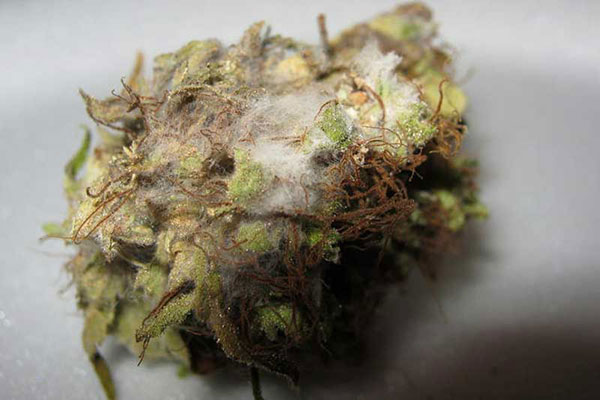

Botrytis is the enemy of the cannabis grower and a harmful fungus that can quickly destroy plants and the crop. Botrytis is a fungal disease that often attacks plants exposed to a cool and humid climate. The disease shows itself by grey and muddy spots on flowers, stems and leaves. If one plant is affected, the fungus can quickly spread to neighbouring plants. Even on already harvested flowers, the harmful fungus can spread even further if the humidity is high enough (above 50%).
Botrytis often starts on and in the flowers and is hardly noticeable at first. Dry and crumbly spots appear in the flowers, which have a grey colour. Botrytis is also the trigger for blight in seedlings. Without countermeasures, the fungus can destroy the entire harvest in indoor growing in only 7-10 days.
Read more about botrytis, how you can recognise the fungus and what you can do against it here:
Breeder/Breeding (Breeding)

The process of producing plants with desirable characteristics is also called breeding. For breeding cannabis plants, it is necessary to know the mechanisms of plant reproduction. Cannabis has a diploid genome, which means that it has two copies of each chromosome in which genes are present. In breeding, a male and a female plant are crossed with each other so that each genetic information can contribute to their offspring.
The complex interaction in selecting desirable traits requires a lot of time, effort and resources from the breeder. Cannabis breeding in common use today began in the 1970s. In breeding projects for new and world-famous cannabis varieties, traits such as potency, yield and aroma are of great importance. Some modern varieties now achieve gigantically high THC content. Many breeders try to stand out by breeding unique flavours and offer varieties that have special characteristics such as high resistance to mould or low growth.
The first generation of progeny resulting from an initial cross between two strains is called an F1 hybrid. The plants can then be re-crossed to further increase certain traits and produce a second generation or F2 hybrid. This process can be repeated several times, securing the best plants from each generation to selectively fix certain traits. To achieve a breeder's goals for the final product, types of breeding used include: Inbred lines and hybrid lines.
Bubble Hash
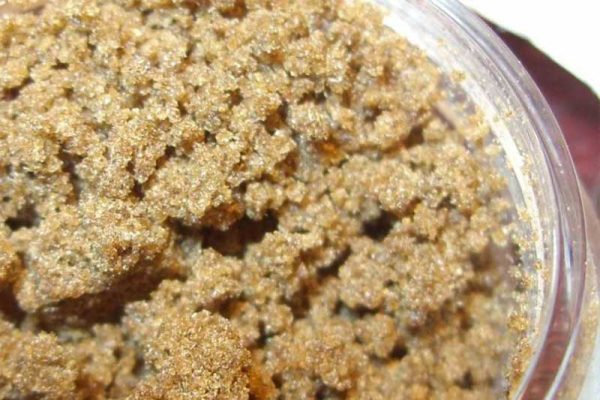

Bubble Hash is a cannabis concentrate consisting of countless trichomes and resin glands. It is made with the help of ice water, a fine mesh micro fabric, agitation and resinous leaflets or flowers. When bubble hash is lit, it often produces crackling sounds - hence its name. The typical textile bags with micro mesh are called Bubble Bags called. Bubble Hash can range from blonde to red to black depending on the quality and varieties used.
Bubble hash came onto the cannabis scene in the mid-1990s and reached the peak of its popularity in the early 2000s. It is still a common and popular method to make very high quality hash yourself.
Bubbler
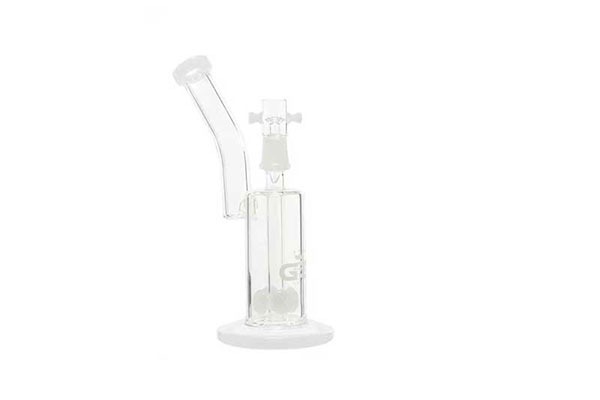

A Bubbler is a hand pipe filled with water and often made of glass. Similar to a bong, the bubbler has a mouthpiece, a tube, a head and a water chamber. Many bubblers have a fixed tube that cannot be removed and some contain a perculator system inside. A bubbler is smaller than most bongs and is ideal for travelling.
Bud
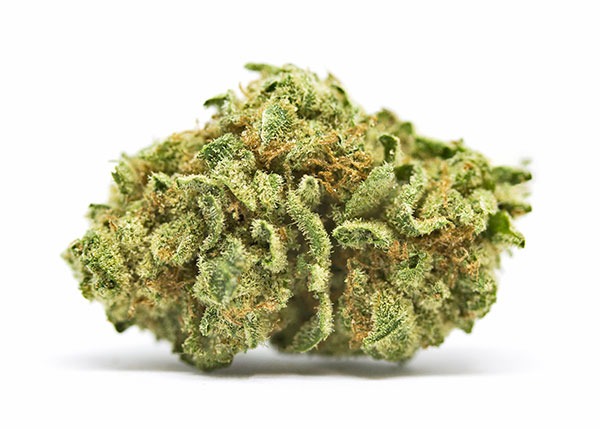

Bud is the smokable and trichome-covered part of the female cannabis flower. It can also be called a collection of calyxes.
Budder
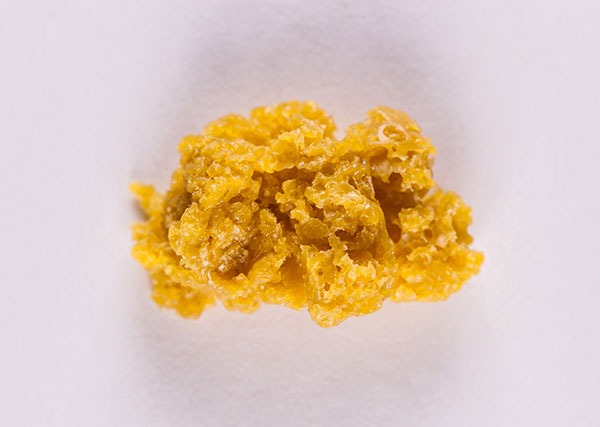

Budder is the name for a cannabis concentrate that contains excessive amounts of terpenes. This makes it more flavourful than other types of cannabis extracts. The extract is called "budder" because of its yellowish and creamy consistency, which resembles butter. During the manufacturing process, the concentrate is vigorously beaten, which creates the creamy texture. Budder is very popular because of its high concentration of THC, which is generally between 80 and 90 percent. Besides the high cannabinoid content, tests have shown that Budder has an ernomen purity level of up to 99%.






