Painful peripheral neuropathy includes several symptoms that severely affect the quality of life of those affected.
These include allodynia (pain triggered by light stimuli that do not normally cause pain) and various sensory disturbances also referred to as numbness: e.g. electric shock sensation, "pins and needles", sensations of cold or warmth, numbness, and other types of unpleasant and painful sensations. Common causes of peripheral neuropathy include diabetes, HIV/AIDS, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, and certain medications or toxins.Treatment usually involves prescribing tricyclic and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), i.e. anti-depressants, anticonvulsants (e.g. barbiturates, benziodiazepines), opioids and certain topical agents. However, many patients only partially benefit from this treatment and some do not tolerate the drugs or do not want to use them because of their side effects. Therefore, the need for effective medication and treatment in this area is very high.
Animal studies and patient testimonials have long indicated that cannabis can be an effective medicine for the treatment of pain and specifically peripheral neuropathy pain. Recently, the Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research (CMCR) at the University of California completed five placebo-controlled II-phase trials. Smoked and vaporised cannabis was used.
Another study from Canada, which included patients suffering from HIV neuropathy and other neuropathic pain, also looked at the issue. In each case, the efficacy of cannabis was found to be comparable to, and in some cases better than, conventionally used medications.
The side effects were only minor and included drowsiness, mild difficulty concentrating and fatigue. Serious side effects (e.g. severe anxiety, paranoia, psychotic symptoms) were not observed.
Neuropathic pain is generally very difficult to treat. Cannabinoids present in cannabis are known to interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the nervous system and have analgesic effects.
The Californian study showed that even a mild treatment with THC (only 3.53% THC) was found to be successful by 61% of the participants. Even a weak dose of 1.29% THC led to a visible improvement for 57% of the participants. The third group had only received a placebo with traces of THC, with 26% of the participants noticing success.
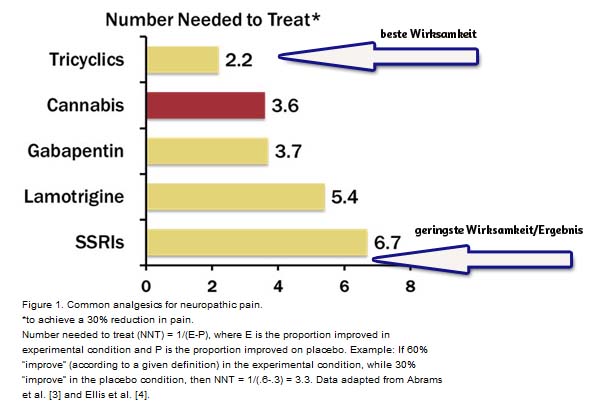
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is not the only cannabinoid with known analgesic effects. The cannabinoids Cannabidiol (CBD) and Cannabichromene (CBC) also has analgesic effects. These mutually reinforce each other when used in combination.
As recent studies show, cannabis and THC can provide improvement in nerve pain, such as that found in multiple sclerosis. In a British study with 66 multiple sclerosis patients suffering from neuropathic pain, the effectiveness of cannabis extract was examined. The patients increased the dose according to their tolerance. After a four-week treatment period, the intensity of the pain of those treated with cannabis was significantly reduced. In addition, sleep also improved. The cannabis extract Sativex was approved in Canada in 2005 for the treatment of nerve pain in adult patients with multiple sclerosis.
Patients with a severance of the plexus of nerves supplying the arm and shoulder (brachial plexus) experience complete paralysis of the arm muscles and loss of sensitivity. Such injuries can be caused, for example, in sports and motorbike accidents. Those affected experience a stabbing and burning pain stimulus in the respective arm, which often lasts for many years. In a study involving 48 patients with such injuries, it was observed that the use of cannabis led to a significant improvement in pain compared to the placebo group.
Cannabis is thus able to relieve various types of nerve pain. Because nerve pain can often only be treated unsatisfactorily with opiates and other painkillers, cannabis could represent a promising and alternative treatment option.
Moreover, cannabis not only works for pain associated with multiple sclerosis, but also improves spasticity, bladder and sleep problems. As summarised by a group of pain specialists on the online research platform MedPanel, cannabis and its cannabinoids represent the most significant new approach to treating neuropathic pain. The potential of cannabinoids with its strong analgesic effect, the broad effect on the central nervous system, the low side effects and the possibility of use in combination with various other forms of treatment show new ways in treatment.
Cannabis strains that have proven successful in the treatment of neuropathic pain:
 Agni Kush( Cannamed)
Agni Kush( Cannamed)
- 20% THC, 4% VBD, 0.9% CBC, 0.4% CBN
- very strong analgesic effect
- Anti-inflammatory, relaxing, sleep-inducing
- for the evening and the night
- Colourful variety with fruity aroma
- 500 g/m², 650 g/plant
- 8-9 weeks flowering / mid-October
Acapulco Gold (Barney's Farm)
- 23% THC
- very good analgesic effect
- Anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxing
- for the evening and the night
- fruity aroma
- 500 g/m²
- 10-11 weeks flowering / mid-October
Canadian Kush (medical Seeds)
- 25% THC
- Most popular variety for pain treatment
- Very low tolerance development
- for the evening and the night
- Sleep-inducing and muscle-relaxing
- large resin content, ideal for concentrates
- 550 g/m²
- 60 days flowering / beginning of October
 CBD Queen (Cannamed)
CBD Queen (Cannamed)
- 9% THC
- 11% CBD
- analgesic and anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic
- No psychedelic effects
- Specially developed for use during the day
- 650 g/m²
- 9 weeks flowering time / beginning of October
Hindu Kush (Sensi Seeds)
- 19%
- very good analgesic effect
- Muscle relaxing and mentally stimulating
- for the evening
- sweet aroma
- 100% Indica
- 45-52 days flowering
- 450 g/m²
Centre for Medicinal Cannabis Research. http://www.cmcr.ucsd.edu.
Pain Clinic Office, Gartnavel General Hospital, University of Glasgow, UK. A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of THC/CBD spray in peripheral neuropathic pain treatment. 2014 European Pain Federation - EFIC®.
<<mehr zum Thema Cannabis als Medizin>>
Medical disclaimer
The information on this website is for general information purposes only and is not to be equated with medical or legal advice. We do not wish to encourage anyone to consume or use drugs illegally. Please consult your doctor/health care provider before using any products/methods referenced or linked to on this website.