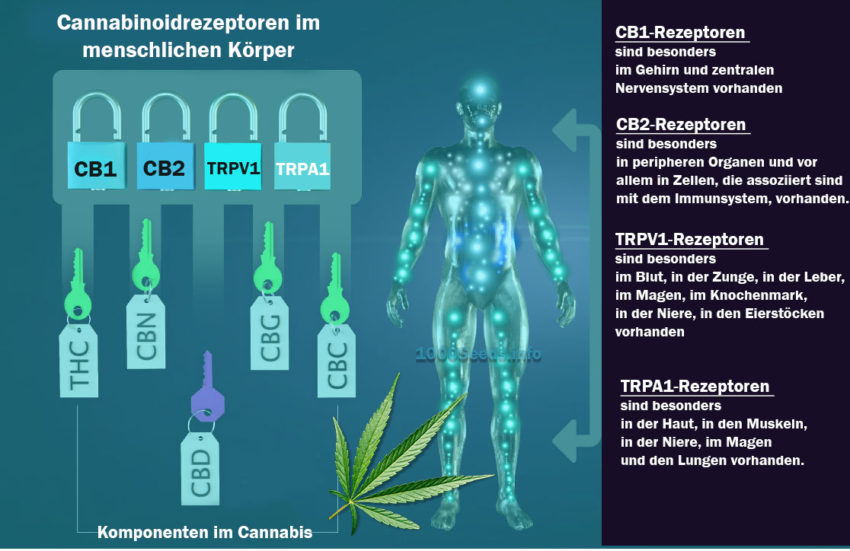
Phytocannabinoids are found in the highest concentrations within the female cannabis flowers, or rather in the resin glands on the surface of the marijuana flowers. The chemical components in cannabis make the plant unique and medicinally valuable. The individual chemical components and cannabinoids cannot be found anywhere else in nature. THC (Delt-9/Delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol) is one of the best known and also most popular cannabinoids with a fun factor, basically the most popular cannabinoid of all. In addition, with the help of research, more than 80 other cannabinoids have been discovered in the marijuana plant in recent years. Most of them are believed to have therapeutic and medicinal effects.
Each individual cannabinoid brings its own specific therapeutic benefits and has its own unique effect on the body's endocannabinoid system. The combination of cannabinoids, as naturally occurring individually in each cannabis plant, results in unique effects and therapeutic efficacy. The user's experience changes depending on the particular cannabinoid combination. For example, a THC-rich Kush strain with a high CBG content makes you feel relaxed and tired. A high THC content with a lot of THCv (tetrahydrocannabivarin), on the other hand, offers an energetic and stimulating high. High levels of CBC and THC often lead to dream-like experiences. In addition, the effect is always dependent on the individual person, their physical and individual conditions. Cannabonoids interact with the cannabinoid receptors in the body and thus produce therapeutic effects.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)

- Formula: C21H30O2
- Molecular weight: 314.2246 g/mol
- Boiling point: 157 °C
THC is the cannabinoid that has been known the longest. As most marijuana lovers probably know, THC is the main psychoactive compound in marijuana. It is responsible for the high and the popular psychoactive effect. THC enhances sensory perception (hearing, seeing, perception of colours...) and gives a feeling of general well-being. THC can also induce strong feelings of euphoria and mental focus and increase creativity. While Δ9-THC is the most common cannabinoid in most dried cannabis flowers, it is far from the only one.
Δ9-THC is the cannabinoid that is also responsible for the famous "munchies" that every cannabis user knows. Surprisingly, the cannabinoid THCv is being researched as an appetite suppressant. THC is the result of THCa decarboxylation. THCa loses carbon molecules and thus becomes the psychoactive THC.
In anorexia nervosa, THC has been shown in studies to be helpful in reversing the weight loss associated with the condition. Both in mice and in humans. Even the synthetic cannabinoids dronabinol and marinol were able to help reduce weight loss. The cannabinoid THC was the first to be found to have a cancer-fighting effect. It could be shown that it can stop the growth of certain cancer cells and in some cases also make them shrink. The exact mode of action and backgrounds have not yet been fully researched. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21412227
The ability of THC to fight tumours in animal models is incredible. THC was the first cannabinoid to be found to have an effect on fighting cancer cells. So far, the full effect and correlations are still not fully understood. Veteran cancer researcher Donald Tashkin, in the largest controlled study of its kind, found that daily smoking of THC-rich cannabis resulted in fewer cancer cases than in the general population of non-smokers. All forms of combustion and smoking produce carcinogens. However, the cannabinoid THC seems to have such powerful and protective effects to prevent the development of cancer more than is caused by smoking. www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/05/25/AR2006052501729.html
In addition, the cannabinoid has other impressive therapeutic benefits. THC is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent. Inflammation is responsible for a whole host of modern diseases. Autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative diseases are health problems in which inflammation plays a major role. The cannabinoid THC is one of the most powerful anti-inflammatory cannabinoids as if it were its very own nature. Therefore, it is also effective against a variety of different diseases.
Cannabinoids like THC induce sleep. At the same time, they also prolong the time in deep sleep. Deep sleep happens in the third and fourth sleep cycles. In deep sleep, the body regenerates and repairs itself. The immune system is recharged in a way.
In a recent case study, a young child suffering from a brain tumour experienced a 90% reduction in tumour size with 2x daily administration of hemp oil. In the treatment of chronic pain, THC treatment shows promising perspectives and seems to change the way nerves function. Especially in neuropathic pain, good results have been achieved through the use of THC. A recent study found that THC changes the perception of pain and makes pain more bearable. It seems to act less like a classic painkiller, reducing the amount of pain felt. Rather, it seems to increase an individual's pain tolerance.
Robert Randall, the first medical cannabis patient in American history and the man responsible for the passage of the federal medical cannabis programme in the US, was treated with THC-rich cannabis in the 1970s to improve intraocular pressure in the eyes. He was on cannabis until his death in 2001. A year after Randall died, a study was conducted that found cannabinoid receptors in the eyes. This in turn provided evidence of THC's efficacy in glaucoma.
THC has numerous medicinal benefits and is therefore now used for many conditions. Here are some examples:
- Alzheimer's
- Neuropathic pain
- Chronic pain
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson's disease
- PTSD
- Cancer
- Crohn's disease
Therapeutic effects of THC
- analgesic
- neuroprotectiv
- anti-inflammatory
- suppresses muscle cramps
- Inhibits the growth of cancer cells
- Stimulates appetite
- decongestant
- relaxing
Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid (THC-A)
- Formula: C22H30O4
- Molecular weight: 358.4733 g/mol
- Boiling point: 105 °C
THC-A, like other cannabinoid acids, is not psychoactive but has strong anti-inflammatory effects, stimulates the appetite, is effective against cancer, insomnia and muscle cramps.
∆8-THC
By THC, most people mean the cannabinoid THC. When, through a process called isomerisation, the atoms are arranged in a different order, ∆8THC is formed. Research has shown that this is also an important cannabinoid.
It is significantly less psychoactive than ∆9THC, its counterpart. ∆8THC and ∆9THC bind to the same CB1 receptors. Because of its low psychoactive effects, it shows promise in treating cancer in children. Some American companies are currently conducting further research on ∆8THC.
The medical effects discovered so far are:
- Reduces nausea
- stimulates the appetite.
learn more about the cannabinoid THC:
Cannabidiol (CBD)
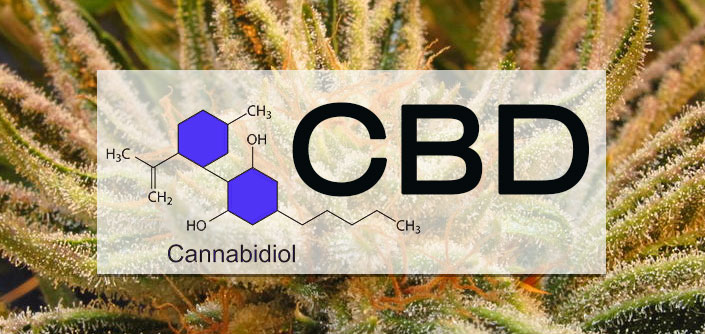
- Formula: C21H30O2
- Molecular weight: 314.2246 g / mol
- Decarboxylation point: 94-145ºC
- Boiling point: 157° C
CBD (cannabidiol) is the second best known cannabinoid. Similar to THC, it offers many medicinal benefits. Unlike THC, CBD is not psychoactive, i.e. it does not produce euphoria or, for example, an altered sense of time. CBD reduces the psychoactive effect of THC and at the same time prolongs the high effect of THC. CBD has significant influence on the human endocannabinoid system.
It has been shown to be extremely valuable in the treatment of seizures such as MS and epilepsy. Because of the non-existent psychoactive effects, it is ideal for treating children, the elderly and patients who prefer to keep a clear head and need to be focused. CBD is used similarly to THC to treat tumours and pain. It lowers blood sugar and is therefore also used in the treatment of diabetes.
CBD has a calming effect and is useful in the treatment of stress-related disorders or sleep problems.
CBD is used, for example, for the following diseases:
- Epilepsy
- MS
- Cancer
- Nausea
- Psychotic illnesses
- Diabetes
- Stress
- Spasms
- therapeutic effects of CBD:
- Decongestant/muscle relaxant
- anti-depressant
- Anti-tumour
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22506672
learn more about the cannabinoid CBD:
-
CBD and its medicinal effect
-
Dosage and use of CBD
-
Social anxiety disorder and treatment with CBD
-
The optimal therapeutic ratio of CBD and THC
Cannabidiolic Acid (CBD-A)
- Formula: C22H30O4
- Molecular weight: 358.2144 g/mol
- Decarboxylate Temperature: 120+ °C (248 °F)
In the past, CBD-A was found in particularly high concentrations, especially in ruderalis. Through hybridisation, many cannabis strains have been created in recent years that produce more CBD-A than THC-A. CBD-A has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-tumour effects.
CBD-A converts very quickly into CBD and is therefore very difficult to capture in its original form. CBD-A and THC-A are the components in cannabis that are present before decarboxylation. These cannabinoids are found in raw, fresh cannabis. They can be ingested when fresh flowers are eaten or mixed into dishes. CBD-A and THC-A can also be applied topically through creams and oils made from fresh flowers.
THC-A and CBD-A cannot be inhaled or smoked. They are rapidly converted by the application of heat.
medicinal effects of CBD-A:
- Anti-bacterial
- Against nausea
- systematically reduces inflammation
- inhibits the growth of cancer cells (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2806496/)
Cannabicyclol (CBL)

- Formula: NA
- Molecular weight: NA g/mol
Cannabicyclol is a breakdown product formed when cannabichromes (CBC) are exposed to light. Little is currently known about its medicinal effects because it occurs in such low concentrations compared to other cannabinoids. This cannabinoid could possibly have an effect on certain muscle tissue.
Cannabichromene (CBC)
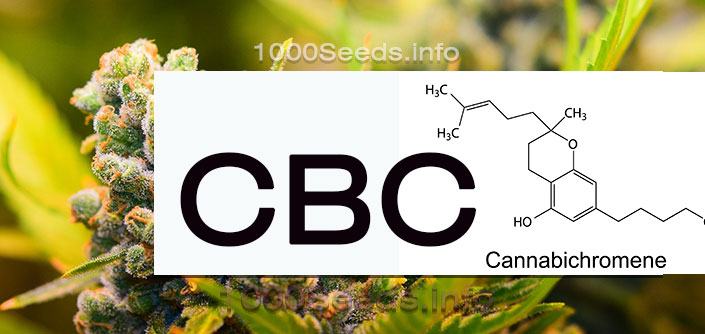
- Formula: C21H30O2
- Molecular weight: 314.2246 g/mol
- Boiling point: 220 °C
Medical effects of CBC
- Anti-mycotic
- anti-inflammatory
- Anti-tumour
- Anti-depressant
- Non psychoactive
- analgesic
- Stimulates bone growth
CBC is the third most abundant cannabinoid in the marijuana plant. Some strains may even have more CBC than CBD. This cannabinoid is also non-psychoactive.
CBC has been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect and, according to a 2010 study, is even more effective when combined with THC. There it is again, the synergistic effect of cannabinoids.
In combination with THC and other cannabinoids, CBC gives hope for effectiveness against breast cancer. Researchers at the University of Mississippi found that CBC has an anti-depressant effect in tests with mice.
A 2013 study found that CBC can help in the creation of new brain cells. In certain areas of the brain, new cells have to be produced again and again in order to maintain the ability to learn and remember. If cells in these areas stop growing or only grow slowly, diseases such as Alzheimer's can occur.
Cannabichromene has been shown to be 10x more effective than CBD in treating stress and anxiety disorders. CBC is also helpful in treating pain and fighting inflammation. It has both anti-viral and anti-tumour effects and stimulates the growth of bone cells.
CBC has the same chemical formula and weight as CBD and THC but differs from its chemical relatives in the arrangement of its atoms. Research on the cannabinoid CBC is still in its infancy. However, its medical potential is already becoming apparent.
The chemical precursor of CBC, CBCa is also attributed with various medicinal effects. It is also anti-bacterial and anti-mycotic.
Probably the most significant discovery to date, CBC has a slowing effect on tumour growth.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20619971
jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/318/3/1375.long
www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0091305710000730
learn more about the cannabinoid CBC:
Cannabinol (CBN)

- Formula: C21H26O2
- Molecular weight: 310.4319 g / mol
- Decarboxylation point: 77 °C
- Boiling point: 185 °C
- Mildly psychoactive
Cannabinol is an oxidation product of THC. It usually forms when THC is exposed to oxygen and heat. A high CBN content often indicates cannabis that is older or has been exposed to greater heat. CBN is very mildly psychoactive and more sedative than many other known cannabinoids.
Indica strains generally seem to have higher CBN levels than sativas. This could also explain why indicas are generally more drowsy and tired. CBN is a CB2 and a CB1 receptor agonist.
Steep Hill Labs state that CBN is one of the most sedative cannabinoids. Already a dose of 2.5-5mg causes a clear and medically relevant sedative effect. So it helps to sleep.
As early as 2002, Swedish researchers found that cannabinol has strong pain-relieving effects. Surprisingly, CBN and THC were the only cannabinoids that fought pain by releasing endorphins and relaxing blood vessels. www.jneurosci.org/content/22/11/4720.full
Due to its strong anti-inflammatory properties, CBN can be helpful in the treatment of asthma, as a 2003 study found.
Medical effects of CBN:
- analgesic
- antibacterial
- Reduces nausea
- anti-inflammatory
- sleep-inducing
- Inhibits the growth of cancer cells
- slightly appetising
- Stimulates bone growth
Both THC and CBN have been identified as painkillers, although THC is far more powerful. A 2002 study found that both THC and CBN cause a release of certain gene-related peptides from sensory nerves, making them the only identified cannabinoids that use this mechanism.
www.jneurosci.org/content/22/11/4720.full
The cannabinoid THC is considered to stimulate the appetite. In 2012, however, it was discovered that CBN can also stimulate the appetite. The effect does not seem to be as strong as with THC.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22543671
A 2006 study found that CBN, THC and numerous other cannabinoids have the ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. CBN in particular was found to control and inhibit a certain type of lung cancer called Lewis carcinoma.
www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/hp/cannabis-pdq#section/all
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16501583?dopt=Abstract
CBN was one of three cannabinoids identified by Italian researchers as effective against resistant MRSA infections.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18681481
learn more about the cannabinoid CBN:
Cannabigerol (CBG)

- Formula: C21H32O2
- Molecular weight: 314.2246 g/mol
- Boiling point: -
Medical effects of CBG:
- Pain-relieving
- Anti-tumour
- Decongesting
- Anti-epileptic
- Sleep-inducing
- Inhibits the growth of cancer cells
- Anti-depressant
- Non psychoactive
This cannabinoid is mainly found in the early growth cycle of the plant. This makes it difficult to obtain in larger quantities. CBG is not psychoactive and is also found in (non-psychoactive) hemp. Cannabigerol has significant medicinal potential, as do many other cannabinoids. CBG has been shown to be more effective against MRSA infection than CBN and is mildly anti-mycotic.
As early as 1982, research found that isolated CBG is antimicrobial and can kill various types of fungi and bacteria. www.researchgate.net/publication/16044956_Synthesis_and_antimicrobial_activities_of_certain_cannabichromene_and_cannabigerol_related_compounds
CBG is considered to have a strong pain-relieving effect, just like THC, and also seems to be helpful in the fight against cancer. Recent research showed that CBG has a mild anti-tumour effect on prostate cancer cells. CBD proved to be even more effective in treating prostate cancer in this study.
CBG was found to be a moderate antidepressant in another study, increasing seratonin levels in the brain. The antidepressant effects of CBG were first discovered in 2006 by Richard Musty and Richard Dayo, who conducted tests with CBG on laboratory rats.
CBG may be a 5-HT1a receptor agonist. The cannabinoid seems to do something at the 5-HT1a receptor that has not been fully understood. It modulates the effects of the other cannabinoids at the appropriate site in the brain, which are related to emotions and depression. This could point to a future treatment option for depression. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC446220/
Some recent studies suggest that CBG may be beneficial for patients with Dravet syndrome. A new tincture has just been released by Harborside Health Center, which is the first CBG-rich tincture on the market. This tincture, called Jayden's Juice after Jayden David, a boy with Dravet syndrome, currently uses CBG instead of pure CBD to treat his seizures.
CBG is believed to be effective in the treatment of seizures. A study from 2013 was able to prove this. However, the exact mechanism behind this has not yet been fully researched.
www.medicinalgenomics.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Voltage-gated-NaV-channel-blockade-by-plant-cannabinoids-does-not-confer-anticonvulsant-effects.pdf
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCv)
- Molecular weight: 314.47 g / mol
- Siedepunkt: < 220 ° C
Medical effects of THCv:
- Analgesic, relieves pain
- Appetite suppressant
- Reduces nausea
- Systematically reduces inflammation
- Promotes bone growth
- Euphoria - Produces feelings of euphoria, promotes happiness and relaxation.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCv) is another cannabinoid that works in tandem with THC. THCv is a non-psychoactive variant of THC. The big difference between the two is that THCv suppresses appetite, whereas THC can stimulate it. For this reason, THCv is being researched as a treatment for obesity. Like many cannabinoids, THCv has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Some studies show that THCv has about 20% of the psychoactive capacity than THC. Recent research has shown that THCV actually attenuates some of the negative psychoactive effects of THC.
THCv is able to significantly reduce seizures and also has a neuroprotective effect. More and more researchers are discovering the link between weight loss and weight regulation and THCv. A combined THCv/CBD tincture was shown in a 2-phase study to be a way to alleviate diabetes.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20196794
www.omicsonline.org/open-access/a-preliminary-understanding-of-cannabis-medicine-and-the-need-for-furthercharacterization-2155-9872-1000275.pdf
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
Until now, there has been little research on CBDv (cannabidivarin). What has been found out so far is promising. CBDv is very similar to CBD, but it is a slightly degraded version of the cannbinoid. The research around this cannabinoid showed evidence that it may have beneficial effects for the treatment of epilepsy.
The medicinal effects of CBDv
- Anti-epileptic
- Against nausea
Two separate studies identified CBDv as a potent anticonvulsant (treatment for epileptic seizures). A 2014 study and other subsequent studies confirmed this finding. This is probably due to its effect on TRPV1 receptors and modulation of gene expression, but needs further research.
CBDv may also likely be helpful for patients with stomach or gastrointestinal problems. In 2013, research at the University of Ontario found that CBDv is helpful for nausea. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23902479